从egg-helper学习egg源码
开发egg-helper插件目的
- 所有的工具函数维护在 app/util 文件内,在使用时需要手动require,如果多个文件使用,需要多个require,致使业务代码实现不优雅
- 在工具函数内部无法直接读取配置文件,通常是使用传参的方式
- Egg也提供Helper框架扩展,但是需将工具函数维护在 app/extend/helper.js 文件内,我更倾向于单独维护
开发经历
第一版
使用egg官方文档提供的loadToContext方法,将 app/helper 内所有文件挂载到ctx.helper对象 loadToContext官方文档,请戳这里
代码实现
// --------egg-helper/app.js -------module.exports = app => { const dir = app.loader.getLoadUnits().map(unit => { return path.join(unit.path, 'app/helper'); }); app.loader.loadToContext(dir, 'helper', { inject: app, call: true, });};...缺点:
- 覆盖掉原有的ctx.helper对象(这里可以选择修改挂载属性名称来避免覆盖,但为了和egg保持一致,所以未选择此方案)
源码学习
打开egg-core工程,根据package.json找到入口文件
...// -------- egg-core/index.js -------module.exports = { EggCore, EggLoader, BaseContextClass, utils,};在index.js文件内,export出四个对象 EggCore: egg核心类
- 继承于koa Application
- 初始化egg Application的对象方法和属性
// -------- egg-core/lib/egg.js -------...class EggCore extends KoaApplication { constructor() { ... const Loader = this[EGG_LOADER]; assert(Loader, "Symbol.for('egg#loader') is required"); this.loader = new Loader({ // 实例化loder,即EggLoader baseDir: options.baseDir, app: this, plugins: options.plugins, logger: this.console, serverScope: options.serverScope, }); const Controller = this.BaseContextClass; this.Controller = Controller; // 定义Controller使用基类 const Service = this.BaseContextClass; this.Service = Service; // 定义Service使用基类 ... }}...EggLoader: egg-core核心类
- 提供load方法,例如loadToContext、loadToApp
- 提供获取egg基础信息方法和属性,例如 getAppInfo
- 挂载 /lib/loader/mixin目录下定义的load函数,具体加载顺序在 egg/lib/loader/appworkerloader.js中定义
// -------- egg-core/lib/loader/egg_loader.js -------class EggLoader { ... // 将property挂载到ctx loadToContext(directory, property, opt) { opt = Object.assign({}, { directory, property, inject: this.app, }, opt);
const timingKey = `Load "${String(property)}" to Context`; this.timing.start(timingKey); new ContextLoader(opt).load(); // 实例化ContextLoader this.timing.end(timingKey); }, // 获取当前 应用/框架/插件下所有文件路径,返回路径数组 getLoadUnits() { if (this.dirs) { return this.dirs; } const dirs = this.dirs = []; // 插入插件路径 if (this.orderPlugins) { for (const plugin of this.orderPlugins) { dirs.push({ path: plugin.path, type: 'plugin', }); } } // 插入框架路径 for (const eggPath of this.eggPaths) { dirs.push({ path: eggPath, type: 'framework', }); } // 插入当前应用路径 dirs.push({ path: this.options.baseDir, type: 'app', }); debug('Loaded dirs %j', dirs); return dirs; } }...const loaders = [ require('./mixin/plugin'), require('./mixin/config'), require('./mixin/extend'), require('./mixin/custom'), require('./mixin/service'), require('./mixin/middleware'), require('./mixin/controller'), require('./mixin/router'),];// 将mixin/*.js文件下的对象挂载EggLoader原型for (const loader of loaders) { Object.assign(EggLoader.prototype, loader);}BaseContextClass 基类,定义了类的属性,Service和Controller都是继承了基类 utils 工具函数
通过Demo来分析helper的挂载和调用
demo/app目录结构如下所示
 调用步骤
调用步骤
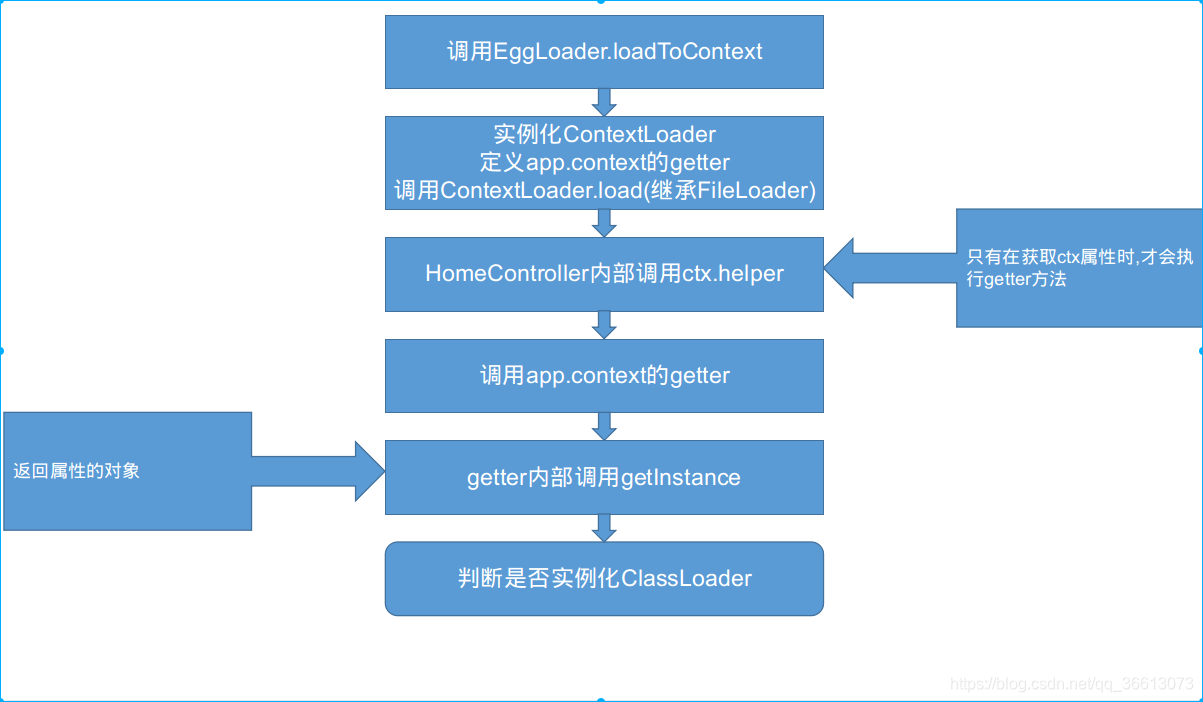
第一步 调用loadToContent
app.loader.loadToContext() // 调用EggLoader实例方法第二步 实例化ContextLoader并调用load方法
ContextLoader继承自FileLoader,FileLoader在下面会讲到
// -------- egg-core/lib/loader/context_loader.js -------
class ContextLoader extends FileLoader { constructor(options) { ... // target在未调用load方法前是空对象 // 在调用load方法后,target是一个以文件层级作为层级的对象,包含文件路径及export出的对象(下面有样本) const target = options.target = {}; if (options.fieldClass) { options.inject[options.fieldClass] = target; } super(options);
const app = this.options.inject; // 当前注入对象 const property = options.property; // 挂载属性名
// 实例化时,使用Object.defineProperty将属性名挂载到app.context上 // 此时仅仅是挂载了属性名,且定义了getter方法,值为空对象 // 当调用了load方法后,才是我们所期望的值 Object.defineProperty(app.context, property, { // 当获取ctx属性时,执行该方法 get() { ... }, }); }}第三步 调用ctx.helper
// -------- demo/app/controller/home.js -------class HomeController extends Controller { async index() { // 在controller中调用工具函数 this.ctx.body =this.ctx.helper.util.demo(); }}第四步 执行getter
此步骤获取ctx属性,执行上一步已定义的getter方法
...// -------- egg-core/lib/loader/context_loader.js -------get() { if (!this[CLASSLOADER]) { // 创建缓存,egg根据每一个请求生成一个Context实例,每个实例不相同 // 缓存根据Context实例生成的,不同实例缓存不同.这里是在同一个实例内,即同一个请求,创建一个缓存 // 在重复获取属性时,避免多次执行getInstance方法 this[CLASSLOADER] = new Map(); } const classLoader = this[CLASSLOADER];
let instance = classLoader.get(property); // 区分当前属性是否被缓存,有缓存就直接返回缓存值 if (!instance) { // 调用getInstance方法 // this指向app.context即ctx instance = getInstance(target, this); // 缓存属性 classLoader.set(property, instance); } return instance;},...第五步 调用getInstance方法
// 调用getInstance的参数values样本// 这也是getter方法内部的target的样本{ util:{ show: [Function: show], [Symbol(EGG_LOADER_ITEM_FULLPATH)]:'.../app/helper/util.js', [Symbol(EGG_LOADER_ITEM_EXPORTS)]: true }, helper:{ util:{ action: [Function: action], [Symbol(EGG_LOADER_ITEM_FULLPATH)]:'.../app/helper/helper/util.js', [Symbol(EGG_LOADER_ITEM_EXPORTS)]: true } }}// -------- egg-core/lib/loader/context_loader.js -------function getInstance(values, ctx) {// 判断当前挂载对象是否是目录,如果是目录,则不含[EXPORTS]属性// 这个属性在FileLoader中定义,下面会介绍 const Class = values[EXPORTS] ? values : null; let instance; if (Class) { if (is.class(Class)) { // 如果是类,则实例化,例如Service // 实例化时会传入ctx对象,所以在Service实例内可以访问ctx对象(这个在基类中有定义) instance = new Class(ctx); } else { // 如果不是类,则直接返回,例如 helper/util.js文件export出的对象 instance = Class; } } else if (is.primitive(values)) { instance = values; } else { // 如果是目录,则实例化ClassLoader,在ClassLoader内部也会调用getInstance方法 // 在ctx上就可以使用 ctx.dirname.dirname.dirname...filename.fn 来调用 // 例如values的样本,最终挂载成 ctx.helper.util.action instance = new ClassLoader({ ctx, properties: values }); } return instance;}
class ClassLoader { constructor(options) { assert(options.ctx, 'options.ctx is required'); const properties = options.properties; // 做缓存,这里的缓存和ContextLoader内的缓存不同 // ContextLoader是对 ctx.property 做缓存 // ClassLoader是对 ctx.property.childProperty[.childProperty...]做缓存 this._cache = new Map(); this._ctx = options.ctx;
for (const property in properties) { // 将属性挂载到ClassLoader实例上 // 通过这个函数实现ctx.dirname.dirname.dirname...filename.fn this.defineProperty(property, properties[property]); } defineProperty(property, values) { Object.defineProperty(this, property, { get() { let instance = this._cache.get(property); if (!instance) { // 虽然在这也会调用getInstance方法,但不会立即执行,只会在执行getter时执行,避免资源浪费 instance = getInstance(values, this._ctx); this._cache.set(property, instance); } return instance; }, }); }}当前版
使用FileLoader实现
调用步骤
代码实现
// --------egg-helper/app.js -------module.exports = app => { const FileLoader = app.loader.FileLoader; const dir = app.loader.getLoadUnits().map(unit => { return path.join(unit.path, 'app/helper'); }); app.loader.loadToContext() new FileLoader({ directory: dir, target: app.Helper.prototype, inject: app, }).load();};...优点
- 不会覆盖原有的ctx.helper对象
源码学习
// -------- egg-core/lib/loader/file_loader.js -------class FileLoader { constructor(options) { assert(options.directory, 'options.directory is required'); assert(options.target, 'options.target is required'); this.options = Object.assign({}, defaults, options);
// 首字母是否小写 if (this.options.lowercaseFirst === true) { deprecate('lowercaseFirst is deprecated, use caseStyle instead'); this.options.caseStyle = 'lower'; } }
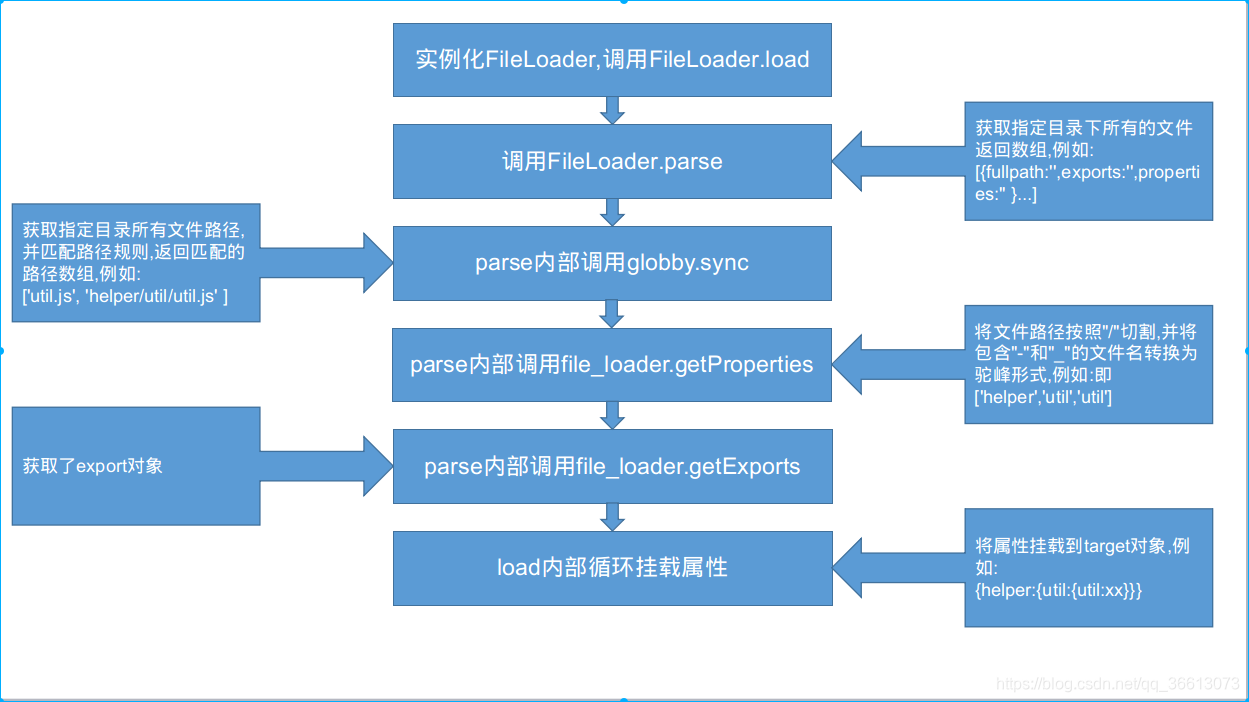
// FileLoader加载文件主方法 // 该方法主要是获取指定目录下文件 // 返回 [{fullpath:"xx",exports:"xx",properties:[xx,yy] }] parse() { // 文件路径匹配,可以查看末尾的options配置 let files = this.options.match; if (!files) { // 是否加载ts files = process.env.EGG_TYPESCRIPT === 'true' && require.extensions['.ts'] ? ['**/*.(js|ts)', '!**/*.d.ts'] : ['**/*.js']; } else { files = Array.isArray(files) ? files : [files]; } // 忽略的文件路径匹配,可以查看末尾的options配置 let ignore = this.options.ignore; if (ignore) { ignore = Array.isArray(ignore) ? ignore : [ignore]; // 路径不为空 ignore = ignore.filter(f => !!f).map(f => '!' + f); files = files.concat(ignore); } // 指定文件的目录,可以查看末尾的options配置 let directories = this.options.directory; if (!Array.isArray(directories)) { directories = [directories]; }
// 文件导出的过滤,可以查看末尾的options配置 const filter = is.function(this.options.filter) ? this.options.filter : null; const items = []; debug('parsing %j', directories); for (const directory of directories) { // 获取指定目录所有文件路径,并匹配上面创建的规则(files),返回匹配的路径数组 const filepaths = globby.sync(files, { cwd: directory }); for (const filepath of filepaths) { const fullpath = path.join(directory, filepath); // 保证当前路径是文件而非目录 if (!fs.statSync(fullpath).isFile()) continue; // 将文件路径按照"/"切割,并将包含"-"和"_"的文件名转换为驼峰形式 const properties = getProperties(filepath, this.options); // 在文件路径前拼上指定的文件目录 const pathName = directory.split(/[/\\]/).slice(-1) + '.' + properties.join('.'); // 加载文件的关键函数 // 获取了export对象,具体信息在下面 const exports = getExports(fullpath, this.options, pathName); // 过滤export if (exports == null || (filter && filter(exports) === false)) continue;
if (is.class(exports)) { exports.prototype.pathName = pathName; exports.prototype.fullPath = fullpath; }
items.push({ fullpath, properties, exports }); debug( 'parse %s, properties %j, export %j', fullpath, properties, exports ); } }
return items; }
// 是FileLoader主方法 // 该方法将指定目录下的所有文件,按照文件层次组成对象(就是上面提到的target对象) load() { // 执行parse方法,获取指定文件目录下所有文件,返回为数组 // 例 [{fullpath:"",exports:"",properties:"" }] const items = this.parse(); // 引用赋值,target改变后,this.options.target也将改变 const target = this.options.target; for (const item of items) { // 通过reduce函数,将target属性不断传递下去,最后形成以文件层级为键名的对象 // 例 {help1:{util1:{...}}} item.properties.reduce((target, property, index) => { let obj; const properties = item.properties.slice(0, index + 1).join('.'); // 当前属性是否为最后一位,如果是最后一位,则代表当前是文件的路径,而非目录 if (index === item.properties.length - 1) { // 防止属性覆盖,同一个文件夹下文件名不允许重复,所以这里主要是防止覆盖掉target对象原来的属性 if (property in target) { if (!this.options.override) throw new Error( `can't overwrite property '${properties}' from ${ target[property][FULLPATH] } by ${item.fullpath}` ); } obj = item.exports; // 如果当前是文件且exports对象不是简单数据类型 if (obj && !is.primitive(obj)) { obj[FULLPATH] = item.fullpath; // 这里的EXPORTS属性,即是在FileLoader里使用的EXPORTS obj[EXPORTS] = true; } } else { // 当前是目录时,如果target不含该属性,则创建空对象 obj = target[property] || {}; } target[property] = obj; debug('loaded %s', properties); return obj; }, target); } return target; }}
// 加载文件function getExports(fullpath, { initializer, call, inject }, pathName) { // 根据路径加载文件,在方法内部存在文件是否为模块的判断: // 如果当前文件扩展名是node不支持的(默认支持*.js,*.node,*.json),则以fs.readFileSync加载,否则以require加载 let exports = utils.loadFile(fullpath); // 自定义export出的对象,可以查看末尾的options配置 if (initializer) { exports = initializer(exports, { path: fullpath, pathName }); } // 判断export出对象的类型,egg规定的export类型有多种,例如 // export default {} export default app=>{} if (is.class(exports) || is.generatorFunction(exports) || is.asyncFunction(exports)) { return exports; } // 判断是否为函数 if (call && is.function(exports)) { // 这一步实现注入对象 // 例如在helper/*.js文件内可以使用app对象 exports = exports(inject); if (exports != null) { return exports; } } return exports;}Helper
Helper声明
// --------egg/lib/application.js -------... get Helper() { if (!this[HELPER]) { // Helper也是继承了BaseContextClass和Service、Controller一样 class Helper extends this.BaseContextClass {} this[HELPER] = Helper; } return this[HELPER]; }...Helper实例化
在框架扩展中加载的
// --------egg/app/extend/context.js -------...get helper() { if (!this[HELPER]) { this[HELPER] = new this.app.Helper(this); } return this[HELPER]; }, ...LoaderOptions
| Param | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| directory | String/Array | directories to be loaded |
| target | Object | attach the target object from loaded files |
| match | String/Array | match the files when load, default to **/*.js |
(if process.env.EGG_TYPESCRIPT was true, default to [ '**/*.(js|ts)', '!**/*.d.ts' ] | ||
| ) | ||
| ignore | String/Array | ignore the files when load |
| initializer | Function | custom file exports, receive two parameters, first is the inject object(if not js file, will be content buffer), second is an options |
object that contain path | ||
| caseStyle | String/Function | set property’s case when converting a filepath to property list. |
| override | Boolean | determine whether override the property when get the same name |
| call | Boolean | determine whether invoke when exports is function |
| inject | Object | an object that be the argument when invoke the function |
| filter | Function | a function that filter the exports which can be loaded |